User Intent – A Guide To Better SEO
How does user intent affect SEO? What does it mean? How can I use it to my advantage?
In this article, you’ll learn about user intent and how to use it to produce content that better satisfy searchers and your organic traffic goals.
TABLE OF CONTENTS 👇
What is intent?
User intent (or search intent) refers to what people are trying to accomplish when they type into a search engine box. For example, if someone types “pizza,” their intention is to eat.
However, if they search “how to make pizza” their intent is to look for a pizza recipe or step-by-step instructions.
Here’s another example.
I typed “golf stand bag reviews” into Google yesterday.
What’s my intent?
To review golf stand bags or to buy a golf stand bag?
To quote Google;
When users type or speak a query, they are trying to accomplish something.
We refer to this as user intent.“
Using the earlier example of “golf stand bag reviews,” what am I trying to accomplish after this search?
A relevant web page would review a list of top golf stand bags, but the page that best satisfies user intent is the page with a recommended product for a man, a woman, and a junior golfer.
This is a simplistic example of user intent.
There are 7 billion searches every day, and it is impossible to classify every query.
Why does intent matter?
Satisfying intent is one of Google’s main goals for its users.
A webpage that matches its content to the user’s intent typically performs better than one designed just for search engines.
Search Quality Rating
In the Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines, Google identifies 4 types of intent:
| Intent | Explanation |
| Know | The intent of a Know query is to find information on a topic. Users want to know more about something.” |
| Do | The intent of a Do query is to accomplish a goal or engage in an activity on a phone. The goal or activity may be to download, to buy, to obtain, to be entertained by, or to interact with a website or app.” |
| Website | The intent of a Website query is to locate a specific website or webpage that users have requested.” |
| Visit | Some queries clearly ‘ask’ for nearby information or nearby results (e.g., businesses, organizations, other nearby places).” |
In this 172-page document, not once does Google mention “search intent”; they mention “user intent” 341 times.
While the Search Quality Rating document is helpful to know how Google thinks, it does not help us produce better content for user intent.
Types of search intent
Many SEO experts classify intent into these 4 buckets.
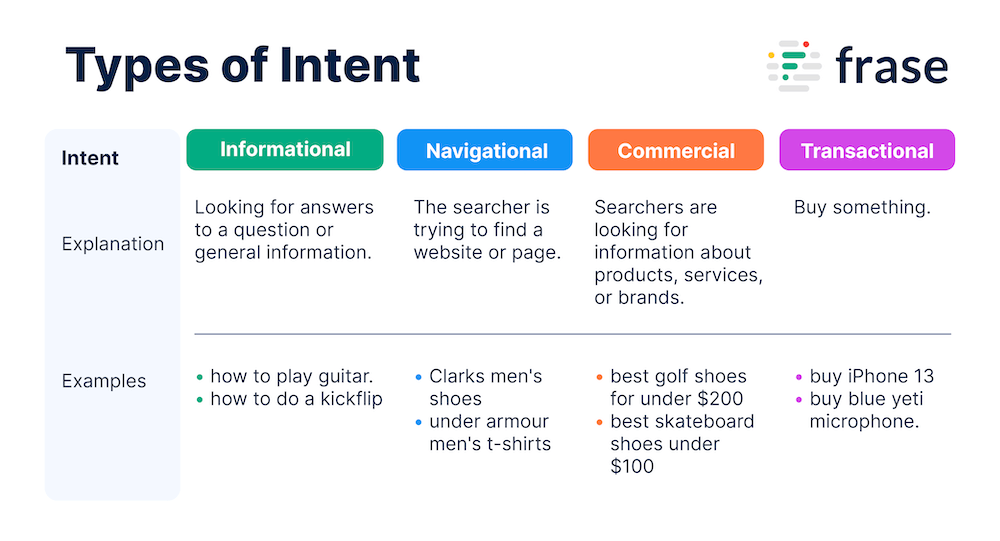
Informational intent
Informational queries such as “how to play guitar”, “how to make a pizza” or “how to create a pivot table in Google Sheets” are made by people looking for answers to a question or general information.
At this stage, they are purely looking for information before progressing to the next stage in the buying process.
However, you may find information boxes called knowledge panels when you search an informational query such as a person or place; this is all part of Google’s strategy to become an answer engine and retain users on Google.
Here’s an example of the knowledge card for the query “what is user intent?” that appears in both text and image format to the right side of the search results.
Navigational intent
A navigational query is where the searcher is trying to find a website or page; for example, “Clarks men’s shoes” or ‘nearest Clark shoe shoes”.
Commercial intent
Commercial queries occur when searchers are looking for information about products, services, or brands.
These commonly have an intent to complete an action or purchase sometime in the future.
For example, “best golf shoes for under $200” or my query with commercial intent, “risk forward book“.
Transactional intent
Transactional queries are those when people have the intention of buying something.
“buy iPhone 13.”
Getting started with intent
The best way to get started with user intent is by Googling the query you want to rank for.
- Read the page titles.
- Read the page descriptions.
Both provide clues about the pages Google favor at the top of the search results.
Then visit a few of the top pages, read the content, and put yourself in the shoes or mind of the user.
Ask, “what do they want next?” or “what would they search for next?“
So, in my example,
I searched “golf stand bag reviews.”
All the top page titles included “golf stand bag reviews.“
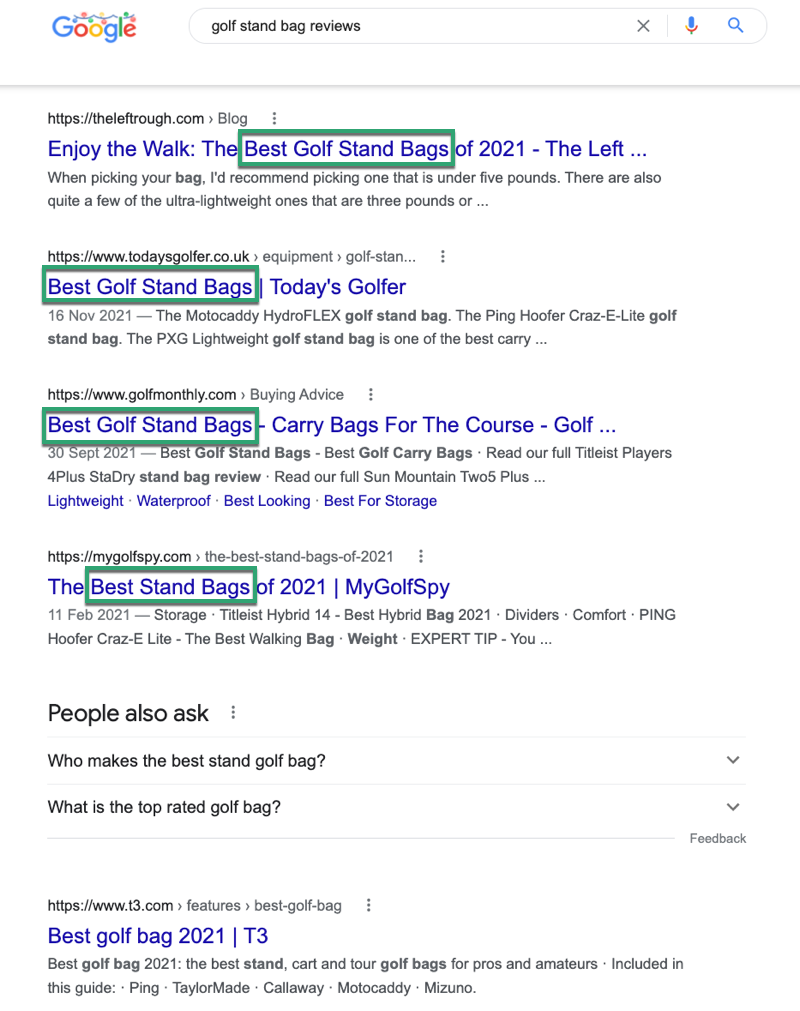
Some of the descriptions mention branded products, best-selling products, and the lightest products.
Perhaps, the user intends to buy the lightest, most popular golf stand bags (amongst the featured products on each page.)
Step 1: Quickly figure out intent
Here at Frase, we believe you can discover a user’s intent much quicker than manually searching Google.
Create a new document with the search query you are targeting.
Look at the SERP tab, and we’ll display the page title, description, and headings of the top pages.
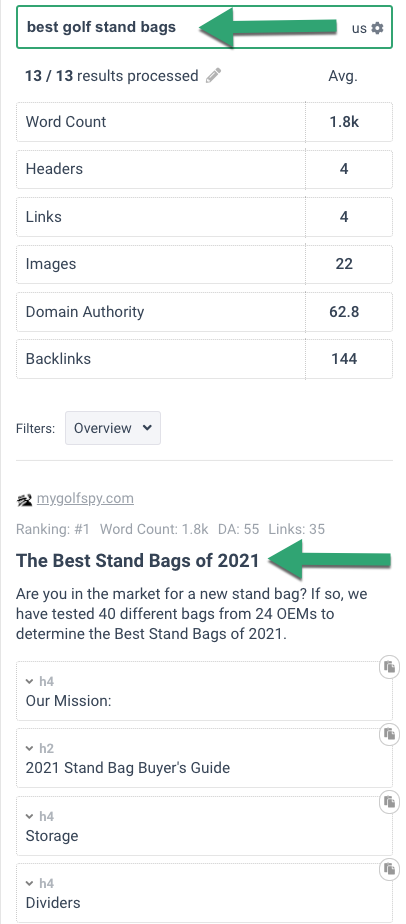
Now look for clues about user intent.
Intent at scale
But what happens when you rank for 15,000 search queries or you’ve done keyword research and identified thousands of opportunities?
How do you infer intent at scale?
SEMRush has recently introduced an intent filter into its keyword research tool.
However, it is an elementary application of a complex subject.
The “Navigational/Informational/Transactional” classification is not particularly helpful for making decisions.
Here are 3 keywords; what do you think their intent is?
1. link building
2. keyword research
3. SEO audit
How would you do anything differently based on the intent assigned by a tool like this?
SEO Testing has assigned a similar intent model for queries you currently rank for.
Step 2: Align content with intent
As Google said, what is the user trying to accomplish after a search?
We can never get into the minds of 5,000 different people searching “golf stand bags reviews” every month.
However, we can align queries with intent and the most appropriate content format to satisfy the user on the page.
Types of user intent
Inside Frase.io, we have created a series of content brief templates to help customers create the right content format for specific search queries.
| Query or page title includes | Intent | Content Format |
| How | The user is searching for instructions to get a result or outcome. | How To Guide |
| What | The user seeks an answer to a question. | What Is Article |
| Best or Top | The user wants to find, use or buy from a recommended list of products, services, or solutions. | Best Post |
| List, Best, Number | The user seeks recommended resources, products, services, and tips | List Post |
| Service | The user wants a service that solves their problem. | Service Page |
| Review | The user is familiar with a product, wishes to know more, or considers purchasing it. | Product Review |
| Comparison, VS | The user wants to see the features and benefits of competing products or services before buying the right one. | Comparison Article |
| Alternatives | Users may know about or are dissatisfied with using a product, service, or company and want another similar solution. | Alternatives Article |
While we haven’t covered every type of user intent to date, these templates will help you create a piece of content with user intent and potential customers in mind.
Step 3: Realign content with intent
Let’s say you launched your website a few years, but you’re not earning the traffic or results you want.
How do you realign your pages and content to satisfy user intent?
First, look for signs of decay.
Pages that have been dropping positions and clicks may have occurred because you’re not addressing intent.
Or else competitors are better serving users.
Content Analytics
In Content Analytics, choose a page with Decay status and review the queries the page ranks for.
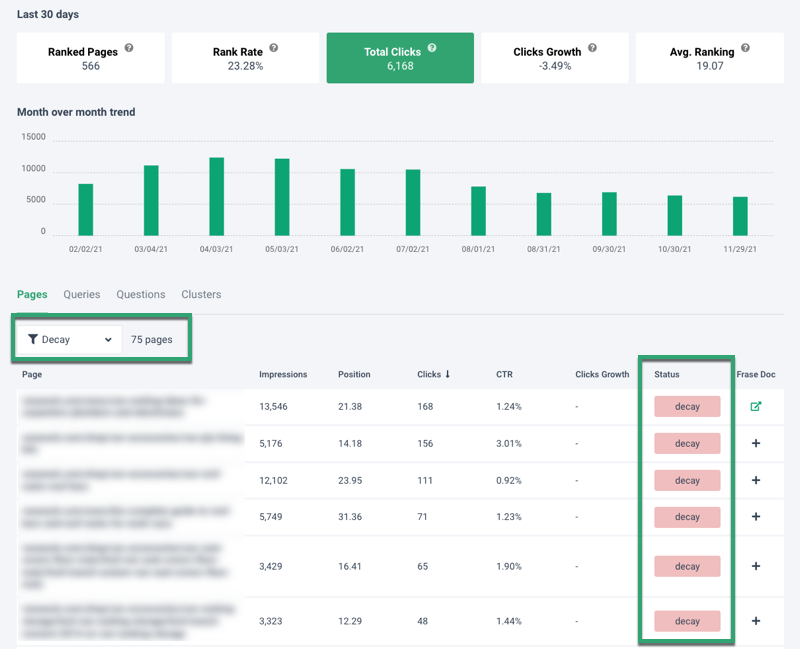
Questions
We display the top questions your website ranks for.
Identify the queries with the most impressions that are not on the first page of Google.
There are 125 impressions for a query in an average position of 26.7 that only gets one click a month in this example.
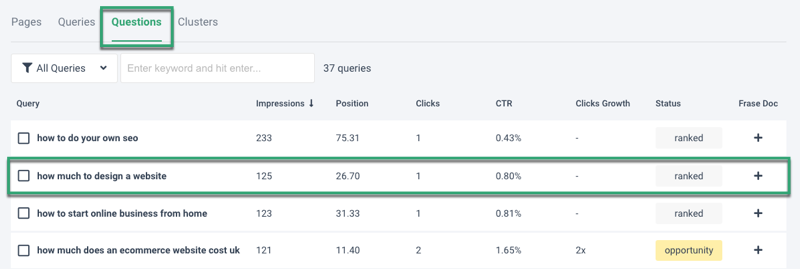
Knowing what you now know about user intent, you can realign your page content to satisfy what the user wants next and boost your click-through rate and organic search traffic.
HOW?
Clusters
We organize the queries you rank for into clusters.
In this example, you can see the top 2 queries the page ranks for.
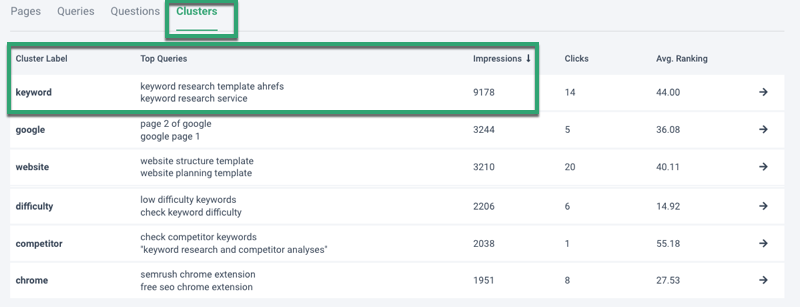
The user intent behind each query is different.
Perhaps a separate page and content are required to address each intent.
Advanced intent realignment
Several tools such as Keyword Cupid and Keyword Insights enables marketers and content creators to use the content cluster model where they group thousand of keywords and create content around search intent.
How to apply user intent to website conversion
Once you understand user intent, how do you use that understanding to optimize conversions?
Conversion refers to optimizing web pages to convert visitors into subscribers, leads or sales.
Let’s say you sell dog products.
Dog owners may better respond to product page images that reflect their breed of dog.
So developing landing pages for the top dog breeds may better match the user’s intent.
Addressing this intent could improve your conversion rates and sales.
Depending on user intent, create different CTA’s and offers.
You need to ensure that your conversion action meets the user’s intent.
For example, if a user enters a how-to query into Google, it’s doubtful that they are ready to hire you for your services.
But you could persuade users to opt-in and receive a copy of your guide.
| Query or page title includes | Intent | CTA Example |
| How | The user is searching for instructions to get a result or outcome. | Download |
| What | The user seeks an answer to a question. | Learn more |
| Best or Top | The user wants to find, use or buy from a recommended list of products, services, or solutions. | Learn more or Buy now |
| List, Best, Number | The user seeks recommended resources, products, services, and tips | Learn more or try a recommendation. |
| Service | The user wants a service that solves their problem. | Contact Us |
| Review | The user is familiar with a product, wishes to know more, or considers purchasing it. | Buy Now |
| Comparison, VS | The user wants to see the features and benefits of competing products or services before buying the right one. | Buy recommended product/service |
| Alternatives | Users may know about or are dissatisfied with using a product, service, or company and want another similar solution. | Buy recommended product/service |
Then you can follow up by email educating the user about how your services help.
You can also optimize your call-to-action (CTA) text for different types of visitors with tools such as RightMessage.
To summarize.
In summary, these are some key takeaways about user intent:
1. The core idea is that user intent is why people visit your web page.
2. You should be asking yourself, “what does my audience want to do after reading my page?”
3. Identifying user intent can shape your content strategy and help you write more relevant high-quality content.
4. Optimizing for user intent can help with user experience, conversion rate optimization, and bounce rate reductions.
5. Create landing pages for each user intent.
6. Use content analytics to identify user intent.
7. Realign content to meet user intent.
8. Make sure your calls-to-action match intent.
Next step
To get started, log in or start a 7-day trial.
